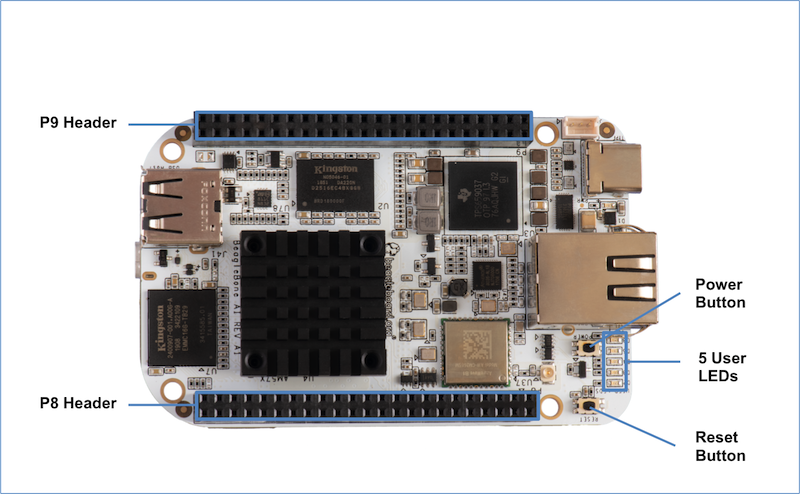
Design and specifications#
This section provides a detailed description of the Hardware design. This can be useful for interfacing, writing drivers, or using it to help modify specifics of your own design.
The figure below is the high level block diagram of BeagleBone® AI. For those who may be concerned, this is the same figure found in section 5. It is placed here again for convenience so it is closer to the topics to follow.
Block Diagram#
The figure below is the high level block diagram of BeagleBone® AI. For detailed layout information please check the schematics.
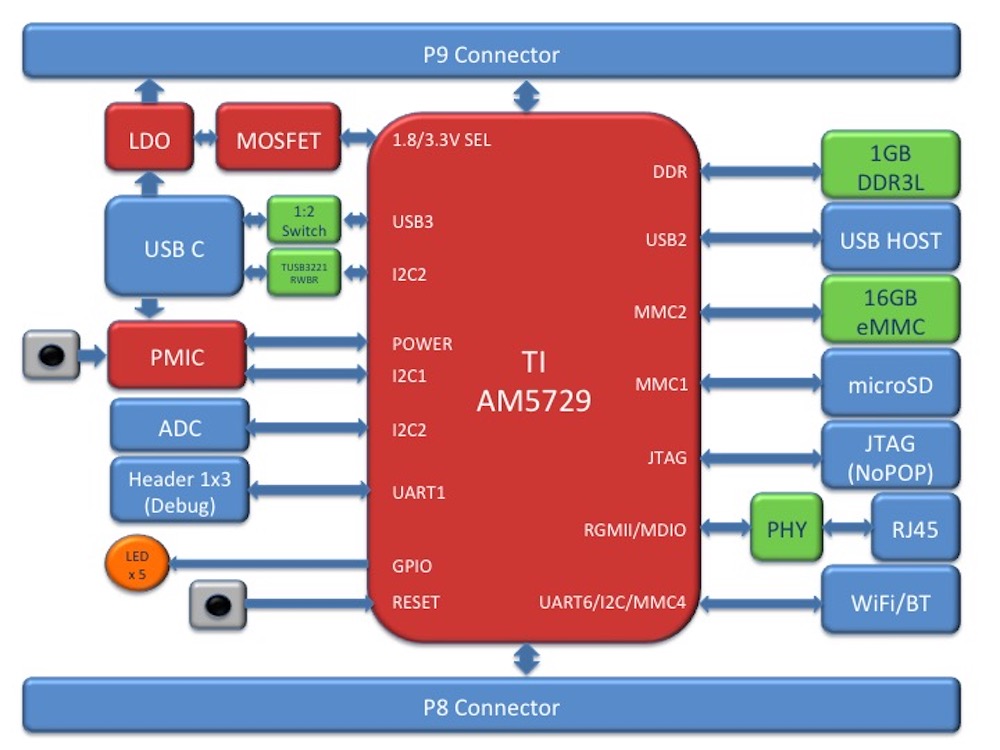
AM572x Sitara™ Processor#
The Texas Instruments AM572x Sitara™ processor family of SOC devices brings high processing performance through the maximum flexibility of a fully integrated mixed processor solution. The devices also combine programmable video processing with a highly integrated peripheral set ideal for AI applications. The AM5729 used on BeagleBone® AI is the super-set device of the family.
Programmability is provided by dual-core ARM® Cortex®-A15 RISC CPUs with Arm® Neon™ extension, and two TI C66x VLIW floating-point DSP core, and Vision AccelerationPac (with 4x EVEs). The Arm allows developers to keep control functions separate from other algorithms programmed on the DSPs and coprocessors, thus reducing the complexity of the system software.
Texas Instruments AM572x Sitara™ Processor Family Block Diagram*
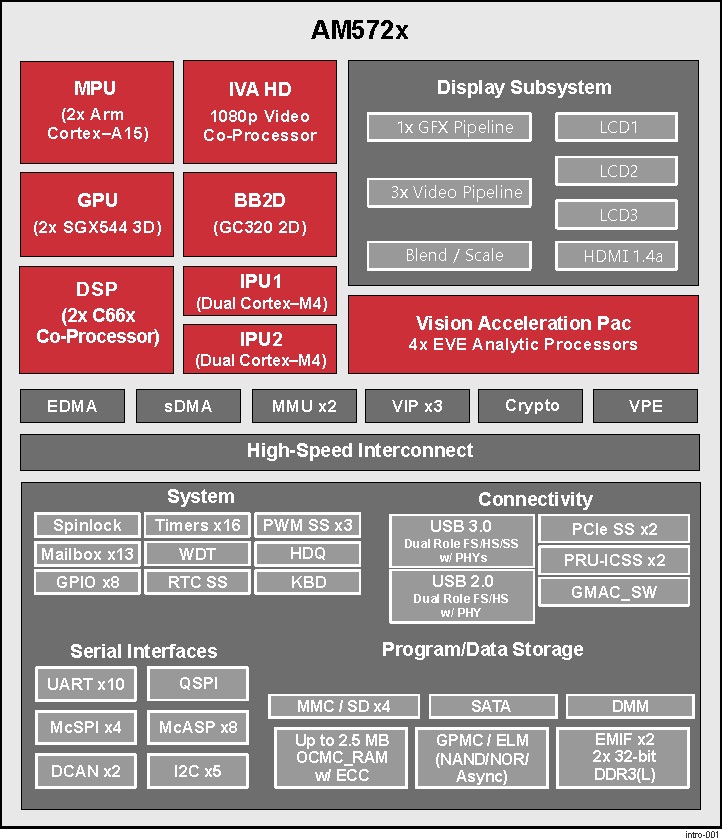
MPU Subsystem The Dual Cortex-A15 MPU subsystem integrates the following submodules:
ARM Cortex-A15 MPCore
Two central processing units (CPUs)
ARM Version 7 ISA: Standard ARM instruction set plus Thumb®-2, Jazelle® RCT Java™ accelerator, hardware virtualization support, and large physical address extensions (LPAE)
Neon™ SIMD coprocessor and VFPv4 per CPU
Interrupt controller with up to 160 interrupt requests
One general-purpose timer and one watchdog timer per CPU – Debug and trace features
32-KiB instruction and 32-KiB data level 1 (L1) cache per CPU
Shared 2-MiB level 2 (L2) cache
48-KiB bootable ROM
Local power, reset, and clock management (PRCM) module
Emulation features
Digital phase-locked loop (DPLL)
DSP Subsystems There are two DSP subsystems in the device. Each DSP subsystem contains the following submodules:
TMS320C66x™ Floating-Point VLIW DSP core for audio processing, and general-purpose imaging and video processing. It extends the performance of existing C64x+™ and C647x™ DSPs through enhancements and new features.
32-KiB L1D and 32-KiB L1P cache or addressable SRAM
288-KiB L2 cache
256-KiB configurable as cache or SRAM
32-KiB SRAM
Enhanced direct memory access (EDMA) engine for video and audio data transfer
Memory management units (MMU) for address management.
Interrupt controller (INTC)
Emulation capabilities
Supported by OpenCL
EVE Subsystems
4 Embedded Vision Engines (EVEs) supported by TIDL machine learning library
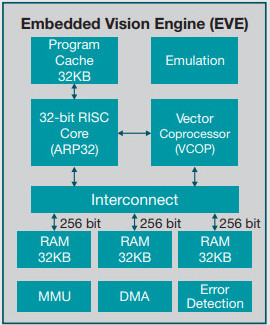
The Embedded Vision Engine (EVE) module is a programmable imaging and vision processing engine. Software support for the EVE module is available through OpenCL Custom Device model with fixed set of functions. More information is available http://www.ti.com/lit/wp/spry251/spry251.pdf
PRU-ICSS Subsystems
2x Dual-Core Programmable Real-Time Unit (PRU) subsystems (4 PRUs total) for ultra low-latency control and software generated peripherals. Access to these powerful subsystems is available through through the P8 and P9 headers. These are detailed in Section 7.
IPU Subsystems There are two Dual Cortex-M4 IPU subsystems in the device available for general purpose usage, particularly real-time control. Each IPU subsystem includes the following components:
Two Cortex-M4 CPUs
ARMv7E-M and Thumb-2 instruction set architectures
Hardware division and single-cycle multiplication acceleration
Dedicated INTC with up to 63 physical interrupt events with 16-level priority
Two-level memory subsystem hierarchy
L1 (32-KiB shared cache memory)
L2 ROM + RAM
64-KiB RAM
16-KiB bootable ROM
MMU for address translation
Integrated power management
Emulation feature embedded in the Cortex-M4
IVA-HD Subsystem
IVA-HD subsystem with support for 4K @ 15fps H.264 encode/decode and other codecs @ 1080p60 The IVA-HD subsystem is a set of video encoder and decoder hardware accelerators. The list of supported codecs can be found in the software development kit (SDK) documentation.
BB2D Graphics Accelerator Subsystem The Vivante® GC320 2D graphics accelerator is the 2D BitBlt (BB2D) graphics accelerator subsystem on the device with the following features:
API support:
OpenWF™, DirectFB
GDI/DirectDraw
BB2D architecture:
BitBlt and StretchBlt
DirectFB hardware acceleration
ROP2, ROP3, ROP4 full alpha blending and transparency
Clipping rectangle support
Alpha blending includes Java 2 Porter-Duff compositing rules
90-, 180-, 270-degree rotation on every primitive
YUV-to-RGB color space conversion
Programmable display format conversion with 14 source and 7 destination formats
High-quality, 9-tap, 32-phase filter for image and video scaling at 1080p
Monochrome expansion for text rendering
32K × 32K coordinate system
Dual-Core PowerVR® SGX544™ 3D GPU The 3D graphics processing unit (GPU) subsystem is based on POWERVR® SGX544 subsystem from Imagination Technologies. It supports general embedded applications. The GPU can process different data types simultaneously, such as: pixel data, vertex data, video data, and general-purpose data. The GPU subsystem has the following features:
Multicore GPU architecture: two SGX544 cores.
Shared system level cache of 128 KiB
Tile-based deferred rendering architecture
Second-generation universal scalable shader engines (USSE2), multithreaded engines incorporating pixel and vertex shader functionality
Present and texture load accelerators
Enables to move, rotate, twiddle, and scale texture surfaces.
Supports RGB, ARGB, YUV422, and YUV420 surface formats.
Supports bilinear upscale.
Supports source colorkey.
Fine-grained task switching, load balancing, and power management
Programmable high-quality image antialiasing
Bilinear, trilinear, anisotropic texture filtering
Advanced geometry DMA driven operation for minimum CPU interaction
Fully virtualized memory addressing for OS operation in a unified memory architecture (MMU)
Memory#
1GB DDR3L#
Dual 256M x 16 DDR3L memory devices are used, one on each side of the board, for a total of 1 GB. They will each operate at a clock frequency of up to 533 MHz yielding an effective rate of 1066Mb/s on the DDR3L bus allowing for 4GB/s of DDR3L memory bandwidth.
16GB Embedded MMC#
A single 16GB embedded MMC (eMMC) device is on the board.
microSD Connector#
The board is equipped with a single microSD connector to act as a secondary boot source for the board and, if selected as such, can be the primary booth source. The connector will support larger capacity microSD cards. The microSD card is not provided with the board.
Boot Modes#
Power Management#
Connectivity#
BeagleBone® AI supports the majority of the functions of the AM5729 SOC through connectors or expansion header pin accessibility. See section 7 for more information on expansion header pinouts. There are a few functions that are not accessible which are: (TBD)
Address |
Identifier |
Description |
|---|---|---|
0x12 |
U3 |
TPS6590379 PMIC DVS |
0x41 |
U78 |
STMPE811Q ADC and GPIO expander |
0x47 |
U13 |
HD3SS3220 USB Type-C DRP port controller |
0x50 |
U9 |
24LC32 board ID EEPROM |
0x58 |
U3 |
TPS6590379 PMIC power registers |
0x5a |
U3 |
TPS6590379 PMIC interfaces and auxiliaries |
0x5c |
U3 |
TPS6590379 PMIC trimming and test |
0x5e |
U3 |
TPS6590379 PMIC OTP |
Power Section#
Figure ? is the high level block diagram of the power section of the board.
(Block Diagram for Power)
TPS6590379 PMIC#
The Texas Instruments TPS6590379ZWSR device is an integrated power-management IC (PMIC) specifically designed to work well ARM Cortex A15 Processors, such as the AM5729 used on BeagleBone® AI. The datasheet is located here https://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/tps659037.pdf
The device provides seven configurable step-down converters with up to 6 A of output current for memory, processor core, input-output (I/O), or preregulation of LDOs. One of these configurable step-down converters can be combined with another 3-A regulator to allow up to 9 A of output current. All of the step-down converters can synchronize to an external clock source between 1.7 MHz and 2.7 MHz, or an internal fallback clock at 2.2 MHz.
The TPS659037 device contains seven LDO regulators for external use. These LDO regulators can be supplied from either a system supply or a preregulated supply. The power-up and power-down controller is configurable and supports any power-up and power-down sequences (OTP based). The TPS659037 device includes a 32-kHz RC oscillator to sequence all resources during power up and power down. In cases where a fast start up is needed, a 16-MHz crystal oscillator is also included to quickly generate a stable 32-kHz for the system. All LDOs and SMPS converters can be controlled by the SPI or I2C interface, or by power request signals. In addition, voltage scaling registers allow transitioning the SMPS to different voltages by SPI, I2C, or roof and floor control.
One dedicated pin in each package can be configured as part of the power-up sequence to control external resources. General-purpose input-output (GPIO) functionality is available and two GPIOs can be configured as part of the power-up sequence to control external resources. Power request signals enable power mode control for power optimization. The device includes a general-purpose sigma-delta analog-to-digital converter (GPADC) with three external input channels.
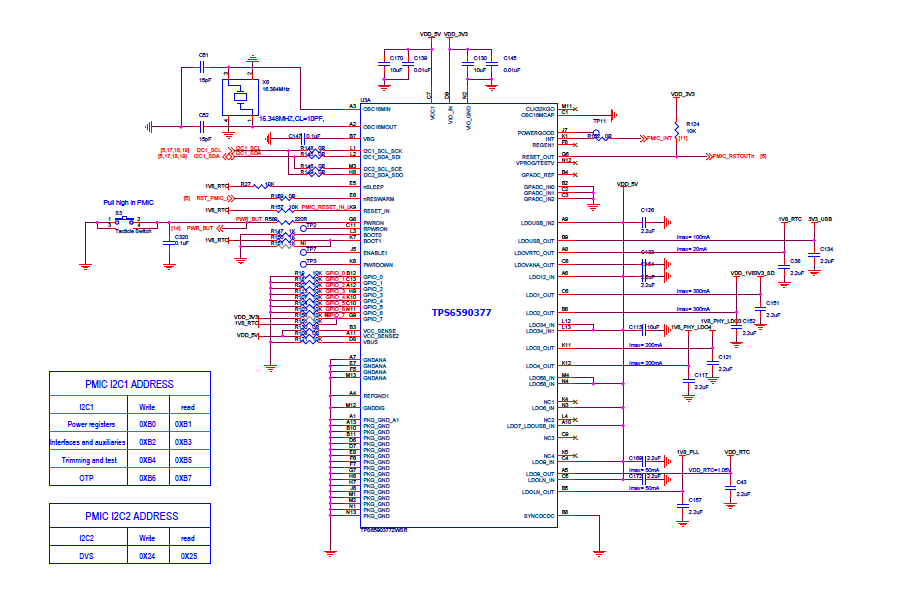
USB-C Power#
Below image shows how the USB-C power input is connected to the TPS6590379.
eMMC Flash Memory (16GB)#
eMMC Device#
eMMC Circuit Design#
Board ID#
A board identifier is placed on the eMMC in the second linear boot partition (/dev/mmcblk1boot1). Reserved bytes up to 32k (0x8000) are filled with “FF”.
Name |
Size (bytes) |
Contents |
|---|---|---|
Header |
4 |
MSB 0xEE3355AA LSB (stored LSB first) |
Board Name |
8 |
Name for board in ASCII “BBONE-AI” = BeagleBone AI |
Version |
4 |
Hardware version code for board in ASCII “00A1” = rev. A1 |
Serial Number |
14 |
Serial number of the board. This is a 14 character string which is: WWYYEMAInnnnnn where:
|
debian@beaglebone:~$ sudo hexdump -C /dev/mmcblk1boot1
00000000 aa 55 33 ee 42 42 4f 4e 45 2d 41 49 30 30 41 31 |.U3.BBONE-AI00A1|
00000010 31 39 33 33 45 4d 41 49 30 30 30 38 30 33 ff ff |1933EMAI000803..|
00000020 ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff ff |................|
*
00008000 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
*
00400000
Wireless Communication: 802.11 ac & Bluetooth: AzureWave AW-CM256SM#
Datasheet https://storage.googleapis.com/wzukusers/user-26561200/documents/5b7d0fe3c3f29Ct6k0QI/AW-CM256SM_DS_Rev%2015_CYW.pdf Wireless connectivity is provided on BeagleBone® AI via the AzureWave Technologies AW-CM256SM IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n/ac Wi-Fi with Bluetooth 4.2 Combo Stamp Module.
This highly integrated wireless local area network (WLAN) solution combines Bluetooth 4.2 and provides a complete 2.4GHz Bluetooth system which is fully compliant to Bluetooth 4.2 and v2.1 that supports EDR of 2Mbps and 3Mbps for data and audio communications. It enables a high performance, cost effective, low power, compact solution that easily fits onto the SDIO and UART combo stamp module.
Compliant with the IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n/ac standard, AW-CM256SM uses Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS), Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM), BPSK, QPSK, CCK and QAM baseband modulation technologies. Compare to 802.11n technology, 802.11ac provides a big improvement on speed and range.
The AW-CM256SM module adopts a Cypress solution. The module design is based on the Cypress CYP43455 single chip.
WLAN on the AzureWave AW-CM256SM#
High speed wireless connection up to 433.3Mbps transmit/receive PHY rate using 80MHz bandwidth,
1 antennas to support 1(Transmit) and 1(Receive) technology and Bluetooth
WCS (Wireless Coexistence System)
Low power consumption and high performance
Enhanced wireless security
Fully speed operation with Piconet and Scatternet support
12mm(L) x 12mm(W) x1.65mm(H) LGA package
Dual - band 2.4 GHz and 5GHz 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac
External Crystal
Bluetooth on the AzureWave AW-CM256S#
1 antennas to support 1(Transmit) and 1(Receive) technology and Bluetooth
Fully qualified Bluetooth BT4.2
Enhanced Data Rate(EDR) compliant for both 2Mbps and 3Mbps supported
High speed UART and PCM for Bluetooth
HDMI#
The HDMI interface is aligned with the HDMI TMDS single stream standard v1.4a (720p @60Hz to 1080p @24Hz) and the HDMI v1.3 (1080p @60Hz): 3 data channels, plus 1 clock channel is supported (differential).
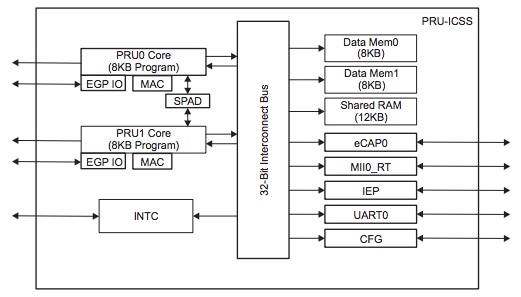
PRU-ICSS#
The Texas Instruments AM5729 Sitara™ provides 2 Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem and Industrial Communciation Subsystems. (PRU-ICSS1 and PRU-ICSS2).
Within each PRU-ICSS are dual 32-bit Load / Store RISC CPU cores: Programmable Real-Time Units (PRU0 and PRU1), shared data and instruction memories, internal peripheral modules and an interrupt controller. Therefore the SoC is providing a total of 4 PRU 32-bit RISC CPU’s:
PRU-ICSS1 PRU0
PRU-ICSS1 PRU1
PRU-ICSS2 PRU0
PRU-ICSS2 PRU1
The programmable nature of the PRUs, along with their access to pins, events and all SoC resources, provides flexibility in implementing fast real-time responses, specialized data handling operations, peripheral interfaces and in off-loading tasks from the other processor cores of the SoC.
PRU-ICSS Features#
Each of the 2 PRU-ICSS (PRU-ICSS1 and PRU-ICSS2) includes the following main features:
2 Independent programmable real-time (PRU) cores (PRU0 and PRU1)
21x Enhanced GPIs (EGPIs) and 21x Enhanced GPOs (EGPOs) with asynchronous capture and serial support per each PRU CPU core
One Ethernet MII_RT module (PRU-ICSS_MII_RT) with two MII ports and configurable connections to PRUs
1 MDIO Port (PRU-ICSS_MII_MDIO)
One Industrial Ethernet Peripheral (IEP) to manage/generate Industrial Ethernet functions
1 x 16550-compatible UART with a dedicated 192 MHz clock to support 12Mbps Profibus
1 Industrial Ethernet timer with 7/9 capture and 8 compare events
1 Enhanced Capture Module (ECAP)
1 Interrupt Controller (PRU-ICSS_INTC)
A flexible power management support
Integrated switched central resource with programmable priority
Parity control supported by all memories
PRU-ICSS Block Diagram#
Below is a high level block diagram of one of the PRU-ICSS Subsystems
PRU-ICSS Resources and FAQ’s#
Resources
Great resources for PRU and BeagleBone® has been compiled here https://beagleboard.org/pru
The PRU Cookbook provides examples and getting started information PRU Cookbook
Detailed specification is available at http://processors.wiki.ti.com/index.php/PRU-ICSS
FAQ
Q: Is it possible to configure the Ethernet MII to be accessed via a PRU MII?
A: TBD
PRU-ICSS1 Pin Access#
The table below shows which PRU-ICSS1 signals can be accessed on BeagleBone® AI and on which connector and pins they are accessible from. Some signals are accessible on the same pins. Signal Names reveal which PRU-ICSS Subsystem is being addressed. pr1 is PRU-ICSS1 and pr2 is PRU-ICSS2
SIGNAL NAME |
DESCRIPTION |
T Y P E |
P R O C |
HE ADER _PIN |
M O D E |
HE ADER _PIN |
M O D E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
pr1_pru0_gpo0 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A H 6 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpo1 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A H 3 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpo2 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A H 5 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpo3 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A G 6 |
P 8_12 |
M O D E 1 3 |
||
pr1_pru0_gpo4 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A H 4 |
P 8_11 |
M O D E 1 3 |
||
pr1_pru0_gpo5 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A G 4 |
P 9_15 |
M O D E 1 3 |
||
pr1_pru0_gpo6 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A G 2 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpo7 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A G 3 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpo8 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A G 5 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpo9 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A F 2 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpo10 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A F 6 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpo11 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A F 3 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpo12 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A F 4 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpo13 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A F 1 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpo14 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A E 3 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpo15 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A E 5 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpo16 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A E 1 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpo17 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A E 2 |
P 9_26 |
M O D E 1 3 |
||
pr1_pru0_gpo18 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A E 6 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpo19 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A D 2 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpo20 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A D 3 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpi0 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A H 6 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpi1 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A H 3 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpi2 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A H 5 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpi3 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A G 6 |
P 8_12 |
M O D E 1 2 |
||
pr1_pru0_gpi4 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A H 4 |
P 8_11 |
M O D E 1 2 |
||
pr1_pru0_gpi5 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A G 4 |
P 9_15 |
M O D E 1 2 |
||
pr1_pru0_gpi6 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A G 2 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpi7 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A G 3 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpi8 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A G 5 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpi9 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A F 2 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpi10 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A F 6 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpi11 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A F 3 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpi12 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A F 4 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpi13 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A F 1 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpi14 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A E 3 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpi15 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A E 5 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpi16 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A E 1 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpi17 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A E 2 |
P 9_26 |
M O D E 1 2 |
||
pr1_pru0_gpi18 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A E 6 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpi19 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A D 2 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru0_gpi20 |
PRU0 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A D 3 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru1_gpo0 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
E 2 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru1_gpo1 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
D 2 |
P 9_20 |
M O D E 1 3 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpo2 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
F 4 |
P 9_19 |
M O D E 1 3 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpo3 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
C 1 |
P 9_41 |
M O D E 1 3 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpo4 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
E 4 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru1_gpo5 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
F 5 |
P 8_18 |
M O D E 1 3 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpo6 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
E 6 |
P 8_19 |
M O D E 1 3 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpo7 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
D 3 |
P 8_13 |
M O D E 1 3 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpo8 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
F 6 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru1_gpo9 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
D 5 |
P 8_14 |
M O D E 1 3 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpo10 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
C 2 |
P 9_42 |
M O D E 1 3 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpo11 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
C 3 |
P 9_27 |
M O D E 1 3 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpo12 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
C 4 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru1_gpo13 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
B 2 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru1_gpo14 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
D 6 |
P 9_14 |
M O D E 1 3 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpo15 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
C 5 |
P 9_16 |
M O D E 1 3 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpo16 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A 3 |
P 8_15 |
M O D E 1 3 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpo17 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
B 3 |
P 8_26 |
M O D E 1 3 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpo18 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
B 4 |
P 8_16 |
M O D E 1 3 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpo19 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
B 5 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru1_gpo20 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Output |
O |
A 4 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru1_gpi0 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
E 2 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru1_gpi1 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
D 2 |
P 9_20 |
M O D E 1 2 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpi2 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
F 4 |
P 9_19 |
M O D E 1 2 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpi3 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
C 1 |
P 9_41 |
M O D E 1 2 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpi4 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
E 4 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru1_gpi5 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
F 5 |
P 8_18 |
M O D E 1 2 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpi6 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
E 6 |
P 8_19 |
M O D E 1 2 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpi7 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
D 3 |
P 8_13 |
M O D E 1 2 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpi8 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
F 6 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru1_gpi9 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
D 5 |
P 8_14 |
M O D E 1 2 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpi10 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
C 2 |
P 9_42 |
M O D E 1 2 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpi11 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
C 3 |
P 9_27 |
M O D E 1 2 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpi12 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
C 4 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru1_gpi13 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
B 2 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru1_gpi14 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
D 6 |
P 9_14 |
M O D E 1 2 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpi15 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
C 5 |
P 9_16 |
M O D E 1 2 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpi16 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A 3 |
P 8_15 |
M O D E 1 2 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpi17 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
B 3 |
P 8_26 |
M O D E 1 2 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpi18 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
B 4 |
P 8_16 |
M O D E 1 2 |
||
pr1_pru1_gpi19 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
B 5 |
NA |
|||
pr1_pru1_gpi20 |
PRU1 G eneral-Purpose Input |
I |
A 4 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mii_mt0_clk |
MII0 Transmit Clock |
I |
U 5 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mii0_txen |
MII0 Transmit Enable |
O |
V 3 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mii0_txd3 |
MII0 Transmit Data |
O |
V 5 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mii0_txd2 |
MII0 Transmit Data |
O |
V 4 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mii0_txd1 |
MII0 Transmit Data |
O |
Y 2 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mii0_txd0 |
MII0 Transmit Data |
O |
W 2 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mii0_rxdv |
MII0 Data Valid |
I |
V 2 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mii_mr0_clk |
MII0 Receive Clock |
I |
Y 1 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mii0_rxd3 |
MII0 Receive Data |
I |
W 9 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mii0_rxd2 |
MII0 Receive Data |
I |
V 9 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mii0_crs |
MII0 Carrier Sense |
I |
V 7 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mii0_rxer |
MII0 Receive Error |
I |
U 7 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mii0_rxd1 |
MII0 Receive Data |
I |
V 6 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mii0_rxd0 |
MII0 Receive Data |
I |
U 6 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mii0_col |
MII0 Collision Detect |
I |
V 1 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mii0_rxlink |
MII0 Receive Link |
I |
U 4 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mii_mt1_clk |
MII1 Transmit Clock |
I |
C 1 |
P 9_41 |
M O D E 1 1 |
||
pr1_mii1_txen |
MII1 Transmit Enable |
O |
E 4 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mii1_txd3 |
MII1 Transmit Data |
O |
F 5 |
P 8_18 |
M O D E 1 1 |
||
pr1_mii1_txd2 |
MII1 Transmit Data |
O |
E 6 |
P 8_19 |
M O D E 1 1 |
||
pr1_mii1_txd1 |
MII1 Transmit Data |
O |
D 5 |
P 8_14 |
M O D E 1 1 |
||
pr1_mii1_txd0 |
MII1 Transmit Data |
O |
C 2 |
P 9_42 |
M O D E 1 1 |
||
pr1_mii_mr1_clk |
MII1 Receive Clock |
I |
C 3 |
P 9_27 |
M O D E 1 1 |
||
pr1_mii1_rxdv |
MII1 Data Valid |
I |
C 4 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mii1_rxd3 |
MII1 Receive Data |
I |
B 2 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mii1_rxd2 |
MII1 Receive Data |
I |
D 6 |
P 9_14 |
M O D E 1 1 |
||
pr1_mii1_rxd1 |
MII1 Receive Data |
I |
C 5 |
P 9_16 |
M O D E 1 1 |
||
pr1_mii1_rxd0 |
MII1 Receive Data |
I |
A 3 |
P 8_15 |
M O D E 1 1 |
||
pr1_mii1_rxer |
MII1 Receive Error |
I |
B 3 |
P 8_26 |
M O D E 1 1 |
||
pr1_mii1_rxlink |
MII1 Receive Link |
I |
B 4 |
P 8_16 |
M O D E 1 1 |
||
pr1_mii1_col |
MII1 Collision Detect |
I |
B 5 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mii1_crs |
MII1 Carrier Sense |
I |
A 4 |
NA |
|||
pr1_mdio_mdclk |
MDIO Clock |
O |
D 3 |
P 8_13 |
M O D E 1 1 |
||
pr1_mdio_data |
MDIO Data |
I O |
F 6 |
NA |
|||
pr1_edc_latch0_in |
Latch Input 0 |
I |
A G 3 / E 2 |
NA |
|||
pr1_edc_latch1_in |
Latch Input 1 |
I |
A G 5 |
NA |
|||
pr1_edc_sync0_out |
SYNC0 Output |
O |
A F 2 / D 2 |
P 9_20 |
M O D E 1 1 |
||
pr1_edc_sync1_out |
SYNC1 Output |
O |
A F 6 |
NA |
|||
pr1_edio_latch_in |
Latch Input |
I |
A F 3 |
NA |
|||
pr1_edio_sof |
Start Of Frame |
O |
A F 4 / F 4 |
P 9_19 |
M O D E 1 1 |
||
pr1_edio_data_in0 |
Ethernet Digital Input |
I |
A F 1 / E 1 |
NA |
|||
pr1_edio_data_in1 |
Ethernet Digital Input |
I |
A E 3 / G 2 |
NA |
|||
pr1_edio_data_in2 |
Ethernet Digital Input |
I |
A E 5 / H 7 |
NA |
|||
pr1_edio_data_in3 |
Ethernet Digital Input |
I |
A E 1 / G 1 |
NA |
|||
pr1_edio_data_in4 |
Ethernet Digital Input |
I |
A E 2 / G 6 |
P 9_26 |
M O D E 1 0 |
P 8_34 |
M O D E 1 2 |
pr1_edio_data_in5 |
Ethernet Digital Input |
I |
A E 6 / F 2 |
P 8_36 |
M O D E 1 2 |
||
pr1_edio_data_in6 |
Ethernet Digital Input |
I |
A D 2 / F 3 |
NA |
|||
pr1_edio_data_in7 |
Ethernet Digital Input |
I |
A D 3 / D 1 |
P 8_15 |
M O D E 1 2 |
||
p r1_edio_data_out0 |
Ethernet Digital Output |
O |
A F 1 / E 1 |
NA |
|||
p r1_edio_data_out1 |
Ethernet Digital Output |
O |
A E 3 / G 2 |
NA |
|||
p r1_edio_data_out2 |
Ethernet Digital Output |
O |
A E 5 / H 7 |
NA |
|||
p r1_edio_data_out3 |
Ethernet Digital Output |
O |
A E 1 / G 1 |
NA |
|||
p r1_edio_data_out4 |
Ethernet Digital Output |
O |
A E 2 / G 6 |
P 9_26 |
M O D E 1 1 |
P 8_34 |
M O D E 1 3 |
p r1_edio_data_out5 |
Ethernet Digital Output |
O |
A E 6 / F 2 |
P 8_36 |
M O D E 1 3 |
||
p r1_edio_data_out6 |
Ethernet Digital Output |
O |
A D 2 / F 3 |
NA |
|||
p r1_edio_data_out7 |
Ethernet Digital Output |
O |
A D 3 / D 1 |
P 8_15 |
M O D E 1 3 |
||
pr1_uart0_cts_n |
UART Clear-To-Send |
I |
G 1 / F 1 1 |
P 8_45 |
M O D E 1 0 |
||
pr1_uart0_rts_n |
UART Ready-To-Send |
O |
G 6 / G 1 0 |
P 8_34 |
M O D E 1 1 |
P 8_46 |
M O D E 1 0 |
pr1_uart0_rxd |
UART Receive Data |
I |
F 2 / F 1 0 |
P 8_36 |
M O D E 1 1 |
P 8_43 |
M O D E 1 0 |
pr1_uart0_txd |
UART Transmit Data |
O |
F 3 / G 1 1 |
P 8_44 |
M O D E 1 0 |
||
pr1_ecap0_ ecap_capin_apwm_o |
Capture Input/PWM Output |
I O |
D 1 / E 9 |
P 8_15 |
M O D E 1 1 |
P 8_41 |
M O D E 1 0 |
PRU-ICSS2 Pin Access#
The table below shows which PRU-ICSS2 signals can be accessed on BeagleBone® AI and on which connector and pins they are accessible from. Some signals are accessible on the same pins. Signal Names reveal which PRU-ICSS Subsystem is being addressed. pr1 is PRU-ICSS1 and pr2 is PRU-ICSS2
SIGNAL NAME |
DESCR IPTION |
TYPE |
PROC |
HEAD ER_PIN |
MODE |
HEAD ER_PIN |
MODE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
p r2_pru 0_gpo0 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
G 11/AC5 |
P8_44 |
MODE13 |
||
p r2_pru 0_gpo1 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
E9/AB4 |
P8_41 |
MODE13 |
||
p r2_pru 0_gpo2 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
F9/AD4 |
P8_42 |
MODE13 |
P8_21 |
MODE13 |
p r2_pru 0_gpo3 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
F8/AC4 |
P8_39 |
MODE13 |
P8_20 |
MODE13 |
p r2_pru 0_gpo4 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
E7/AC7 |
P8_40 |
MODE13 |
P8_25 |
MODE13 |
p r2_pru 0_gpo5 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
E8/AC6 |
P8_37 |
MODE13 |
P8_24 |
MODE13 |
p r2_pru 0_gpo6 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
D9/AC9 |
P8_38 |
MODE13 |
P8_5 |
MODE13 |
p r2_pru 0_gpo7 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
D7/AC3 |
P8_36 |
MODE13 |
P8_6 |
MODE13 |
p r2_pru 0_gpo8 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
D8/AC8 |
P8_34 |
MODE13 |
P8_23 |
MODE13 |
p r2_pru 0_gpo9 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
A5/AD6 |
P8_35 |
MODE13 |
P8_22 |
MODE13 |
pr 2_pru0 _gpo10 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
C6/AB8 |
P8_33 |
MODE13 |
P8_3 |
MODE13 |
pr 2_pru0 _gpo11 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
C8/AB5 |
P8_31 |
MODE13 |
P8_4 |
MODE13 |
pr 2_pru0 _gpo12 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
C7/B18 |
P8_32 |
MODE13 |
||
pr 2_pru0 _gpo13 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
B7/F15 |
P8_45 |
MODE13 |
||
pr 2_pru0 _gpo14 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
B8/B19 |
P9_11 |
MODE13 |
P9_11 |
MODE13 |
pr 2_pru0 _gpo15 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
A7/C17 |
P8_17 |
MODE13 |
P9_13 |
MODE13 |
pr 2_pru0 _gpo16 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
A8/C15 |
P8_27 |
MODE13 |
||
pr 2_pru0 _gpo17 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
C9/A16 |
P8_28 |
MODE13 |
||
pr 2_pru0 _gpo18 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
A9/A19 |
P8_29 |
MODE13 |
||
pr 2_pru0 _gpo19 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
B9/A18 |
P8_30 |
MODE13 |
||
pr 2_pru0 _gpo20 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
A 10/F14 |
P8_46 |
MODE13 |
P8_8 |
MODE13 |
p r2_pru 0_gpi0 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
G 11/AC5 |
P8_44 |
MODE12 |
||
p r2_pru 0_gpi1 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
E9/AB4 |
P8_41 |
MODE12 |
||
p r2_pru 0_gpi2 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
F9/AD4 |
P8_42 |
MODE12 |
P8_21 |
MODE12 |
p r2_pru 0_gpi3 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
F8/AC4 |
P8_39 |
MODE12 |
P8_20 |
MODE12 |
p r2_pru 0_gpi4 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
E7/AC7 |
P8_40 |
MODE12 |
P8_25 |
MODE12 |
p r2_pru 0_gpi5 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
E8/AC6 |
P8_37 |
MODE12 |
P8_24 |
MODE12 |
p r2_pru 0_gpi6 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
D9/AC9 |
P8_38 |
MODE12 |
P8_5 |
MODE12 |
p r2_pru 0_gpi7 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
D7/AC3 |
P8_36 |
MODE12 |
P8_6 |
MODE12 |
p r2_pru 0_gpi8 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
D8/AC8 |
P8_34 |
MODE12 |
P8_23 |
MODE12 |
p r2_pru 0_gpi9 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
A5/AD6 |
P8_35 |
MODE12 |
P8_22 |
MODE12 |
pr 2_pru0 _gpi10 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
C6/AB8 |
P8_33 |
MODE12 |
P8_3 |
MODE12 |
pr 2_pru0 _gpi11 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
C8/AB5 |
P8_31 |
MODE12 |
P8_4 |
MODE12 |
pr 2_pru0 _gpi12 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
C7/B18 |
P8_32 |
MODE12 |
||
pr 2_pru0 _gpi13 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
B7/F15 |
P8_45 |
MODE12 |
||
pr 2_pru0 _gpi14 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
B8/B19 |
P9_11 |
MODE12 |
P9_11 |
MODE12 |
pr 2_pru0 _gpi15 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
A7/C17 |
P8_17 |
MODE12 |
P9_13 |
MODE12 |
pr 2_pru0 _gpi16 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
A8/C15 |
P8_27 |
MODE12 |
||
pr 2_pru0 _gpi17 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
C9/A16 |
P8_28 |
MODE12 |
||
pr 2_pru0 _gpi18 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
A9/A19 |
P8_29 |
MODE12 |
||
pr 2_pru0 _gpi19 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
B9/A18 |
P8_30 |
MODE12 |
||
pr 2_pru0 _gpi20 |
PRU0 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
A 10/F14 |
P8_46 |
MODE12 |
P8_8 |
MODE12 |
p r2_pru 1_gpo0 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
V1/D17 |
P8_32 |
MODE13 |
||
p r2_pru 1_gpo1 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
U4/AA3 |
NA |
|||
p r2_pru 1_gpo2 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
U3/AB9 |
NA |
|||
p r2_pru 1_gpo3 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
V2/AB3 |
NA |
|||
p r2_pru 1_gpo4 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
Y1/AA4 |
NA |
|||
p r2_pru 1_gpo5 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
W9/D18 |
P9_25 |
MODE13 |
||
p r2_pru 1_gpo6 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
V9/E17 |
P8_9 |
MODE13 |
||
p r2_pru 1_gpo7 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
V7/C14 |
P9_31 |
MODE13 |
||
p r2_pru 1_gpo8 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
U7/G12 |
P9_18 |
MODE13 |
||
p r2_pru 1_gpo9 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
V6/F12 |
P9_17 |
MODE13 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpo10 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
U6/B12 |
P9_31 |
MODE13 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpo11 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
U5/A11 |
P9_29 |
MODE13 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpo12 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
V5/B13 |
P9_30 |
MODE13 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpo13 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
V4/A12 |
P9_26 |
MODE13 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpo14 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
V3/E14 |
P9_42 |
MODE13 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpo15 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
Y2/A13 |
P8_10 |
MODE13 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpo16 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
W2/G14 |
P8_7 |
MODE13 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpo17 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
E11 |
P8_27 |
MODE13 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpo18 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
F11 |
P8_45 |
MODE13 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpo19 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
G10 |
P8_46 |
MODE13 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpo20 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Output |
O |
F10 |
P8_43 |
MODE13 |
||
p r2_pru 1_gpi0 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
V1/D17 |
P8_32 |
MODE12 |
||
p r2_pru 1_gpi1 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
U4/AA3 |
NA |
|||
p r2_pru 1_gpi2 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
U3/AB9 |
NA |
|||
p r2_pru 1_gpi3 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
V2/AB3 |
NA |
|||
p r2_pru 1_gpi4 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
Y1/AA4 |
NA |
|||
p r2_pru 1_gpi5 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
W9/D18 |
P9_25 |
MODE12 |
||
p r2_pru 1_gpi6 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
V9/E17 |
P8_9 |
MODE12 |
||
p r2_pru 1_gpi7 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
V7/C14 |
P9_31 |
MODE12 |
||
p r2_pru 1_gpi8 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
U7/G12 |
P9_18 |
MODE12 |
||
p r2_pru 1_gpi9 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
V6/F12 |
P9_17 |
MODE12 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpi10 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
U6/B12 |
P9_31 |
MODE12 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpi11 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
U5/A11 |
P9_29 |
MODE12 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpi12 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
V5/B13 |
P9_30 |
MODE12 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpi13 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
V4/A12 |
P9_28 |
MODE12 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpi14 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
V3/E14 |
P9_42 |
MODE12 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpi15 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
Y2/A13 |
P8_10 |
MODE12 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpi16 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
W2/G14 |
P8_7 |
MODE12 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpi17 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
E11 |
P8_27 |
MODE12 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpi18 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
F11 |
P8_45 |
MODE12 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpi19 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
G10 |
P8_46 |
MODE12 |
||
pr 2_pru1 _gpi20 |
PRU1 Gen eral-P urpose Input |
I |
F10 |
P8_43 |
MODE12 |
||
pr2_e dc_lat ch0_in |
Latch Input 0 |
I |
F9 |
P8_42 |
MODE10 |
||
pr2_e dc_lat ch1_in |
Latch Input 1 |
I |
F8 |
P8_39 |
MODE10 |
||
pr2_e dc_syn c0_out |
SYNC0 Output |
O |
E7 |
P8_40 |
MODE10 |
||
pr2_e dc_syn c1_out |
SYNC1 Output |
O |
E8 |
P8_37 |
MODE10 |
||
pr2_e dio_la tch_in |
Latch Input |
I |
D9 |
P8_38 |
MODE10 |
||
pr2_ed io_sof |
Start Of Frame |
O |
D7 |
P8_36 |
MODE10 |
||
pr2 _uart0 _cts_n |
UART C lear-T o-Send |
I |
D8 |
P8_34 |
MODE10 |
||
pr2 _uart0 _rts_n |
UART R eady-T o-Send |
O |
A5 |
P8_35 |
MODE10 |
||
p r2_uar t0_rxd |
UART R eceive Data |
I |
C6 |
P8_33 |
MODE10 |
||
p r2_uar t0_txd |
UART Tr ansmit Data |
O |
C8 |
P8_31 |
MODE10 |
||
pr2 _ecap0 _ecap_ capin_ apwm_o |
C apture Inp ut/PWM output |
IO |
C7 |
P8_32 |
MODE10 |
||
pr2_e dio_da ta_in0 |
Et hernet D igital Input |
I |
B7 |
P8_45 |
MODE10 |
||
pr2_e dio_da ta_in1 |
Et hernet D igital Input |
I |
B8 |
P9_11 |
MODE10 |
||
pr2_e dio_da ta_in2 |
Et hernet D igital Input |
I |
A7 |
P8_17 |
MODE10 |
||
pr2_e dio_da ta_in3 |
Et hernet D igital Input |
I |
A8 |
P8_27 |
MODE10 |
||
pr2_e dio_da ta_in4 |
Et hernet D igital Input |
I |
C9 |
P8_28 |
MODE10 |
||
pr2_e dio_da ta_in5 |
Et hernet D igital Input |
I |
A9 |
P8_29 |
MODE10 |
||
pr2_e dio_da ta_in6 |
Et hernet D igital Input |
I |
B9 |
P8_30 |
MODE10 |
||
pr2_e dio_da ta_in7 |
Et hernet D igital Input |
I |
A10 |
P8_46 |
MODE10 |
||
pr2_ed io_dat a_out0 |
Et hernet D igital Output |
O |
B7 |
P8_45 |
MODE11 |
||
pr2_ed io_dat a_out1 |
Et hernet D igital Output |
O |
B8 |
P9_11 |
MODE11 |
||
pr2_ed io_dat a_out2 |
Et hernet D igital Output |
O |
A7 |
P8_17 |
MODE11 |
||
pr2_ed io_dat a_out3 |
Et hernet D igital Output |
O |
A8 |
P8_27 |
MODE11 |
||
pr2_ed io_dat a_out4 |
Et hernet D igital Output |
O |
C9 |
P8_28 |
MODE11 |
||
pr2_ed io_dat a_out5 |
Et hernet D igital Output |
O |
A9 |
P8_29 |
MODE11 |
||
pr2_ed io_dat a_out6 |
Et hernet D igital Output |
O |
B9 |
P8_30 |
MODE11 |
||
pr2_ed io_dat a_out7 |
Et hernet D igital Output |
O |
A10 |
P8_46 |
MODE11 |
||
pr2_mi i1_col |
MII1 Col lision Detect |
I |
D18 |
P9_25 |
MODE11 |
||
pr2_mi i1_crs |
MII1 C arrier Sense |
I |
E17 |
P8_9 |
MODE11 |
||
pr 2_mdio _mdclk |
MDIO Clock |
O |
C 14/AB3 |
P9_31 |
MODE11 |
||
p r2_mdi o_data |
MDIO Data |
IO |
D 14/AA4 |
P9_29 |
MODE11 |
||
p r2_mii 0_rxer |
MII0 R eceive Error |
I |
G12 |
P9_18 |
MODE11 |
||
pr2 _mii_m t0_clk |
MII0 Tr ansmit Clock |
I |
F12 |
P9_17 |
MODE11 |
||
p r2_mii 0_txen |
MII0 Tr ansmit Enable |
O |
B12 |
P9_31 |
MODE11 |
||
p r2_mii 0_txd3 |
MII0 Tr ansmit Data |
O |
A11 |
P9_29 |
MODE11 |
||
p r2_mii 0_txd2 |
MII0 Tr ansmit Data |
O |
B13 |
P9_30 |
MODE11 |
||
p r2_mii 0_txd1 |
MII0 Tr ansmit Data |
O |
A12 |
P9_28 |
MODE11 |
||
p r2_mii 0_txd0 |
MII0 Tr ansmit Data |
O |
E14 |
P9_42 |
MODE11 |
||
pr2 _mii_m r0_clk |
MII0 R eceive Clock |
I |
A13 |
P8_10 |
MODE11 |
||
p r2_mii 0_rxdv |
MII0 Data Valid |
I |
G14 |
P8_7 |
MODE11 |
||
p r2_mii 0_rxd3 |
MII0 R eceive Data |
I |
F14 |
P8_8 |
MODE11 |
||
p r2_mii 0_rxd2 |
MII0 R eceive Data |
I |
A19 |
NA |
|||
p r2_mii 0_rxd1 |
MII0 R eceive Data |
I |
A18 |
NA |
|||
p r2_mii 0_rxd0 |
MII0 R eceive Data |
I |
C15 |
NA |
|||
pr2 _mii0_ rxlink |
MII0 R eceive Link |
I |
A16 |
NA |
|||
pr2_mi i0_crs |
MII0 C arrier Sense |
I |
B18 |
NA |
|||
pr2_mi i0_col |
MII0 Col lision Detect |
I |
F15 |
NA |
|||
p r2_mii 1_rxer |
MII1 R eceive Error |
I |
B19 |
P9_11 |
MODE11 |
||
pr2 _mii1_ rxlink |
MII1 R eceive Link |
I |
C17 |
P9_13 |
MODE11 |
||
pr2 _mii_m t1_clk |
MII1 Tr ansmit Clock |
I |
AC5 |
NA |
|||
p r2_mii 1_txen |
MII1 Tr ansmit Enable |
O |
AB4 |
NA |
|||
p r2_mii 1_txd3 |
MII1 Tr ansmit Data |
O |
AD4 |
P8_21 |
MODE11 |
||
p r2_mii 1_txd2 |
MII1 Tr ansmit Data |
O |
AC4 |
P8_20 |
MODE11 |
||
p r2_mii 1_txd1 |
MII1 Tr ansmit Data |
O |
AC7 |
P8_25 |
MODE11 |
||
p r2_mii 1_txd0 |
MII1 Tr ansmit Data |
O |
AC6 |
P8_24 |
MODE11 |
||
pr2 _mii_m r1_clk |
MII1 R eceive Clock |
I |
AC9 |
P8_5 |
MODE11 |
||
p r2_mii 1_rxdv |
MII1 Data Valid |
I |
AC3 |
P8_6 |
MODE11 |
||
p r2_mii 1_rxd3 |
MII1 R eceive Data |
I |
AC8 |
P8_23 |
MODE11 |
||
p r2_mii 1_rxd2 |
MII1 R eceive Data |
I |
AD6 |
P8_22 |
MODE11 |
||
p r2_mii 1_rxd1 |
MII1 R eceive Data |
I |
AB8 |
P8_3 |
MODE11 |
||
p r2_mii 1_rxd0 |
MII1 R eceive Data |
I |
AB5 |
P8_4 |
MODE11 |
||
end |
end |
end |
end |
end |
end |
end |
end |
User LEDs#
There are 5 User Programmable LEDs on BeagleBone® AI. These are connected to GPIO pins on the processor.
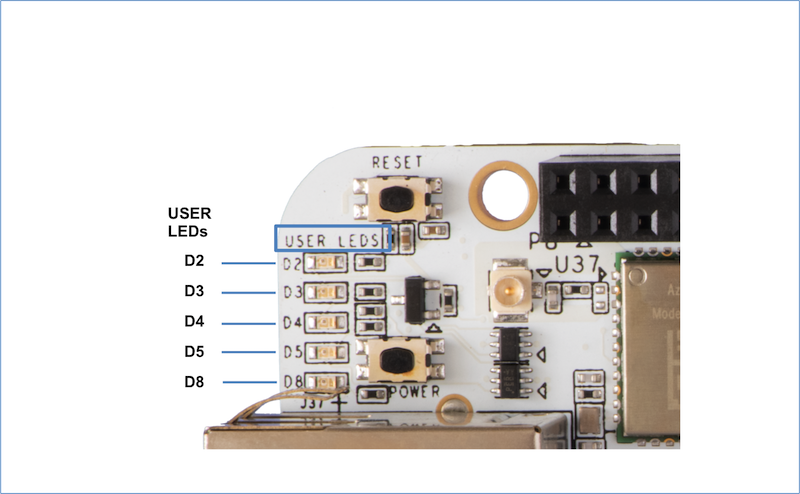
The table shows the signals used to control the LEDs from the processor. Each LED is user programmable. However, there is a Default Functions assigned in the device tree for BeagleBone® AI:
LED |
GPIO SIGNAL |
DEFAULT FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|
D2 |
GPIO3_17 |
Heartbeat When Linux is Running |
D3 |
GPIO5_5 |
microSD Activity |
D4 |
GPIO3_15 |
CPU Activity |
D5 |
GPIO3_14 |
eMMC Activity |
D8 |
GPIO3_7 |
WiFi/Bluetooth Activity |